Biology Diagrams
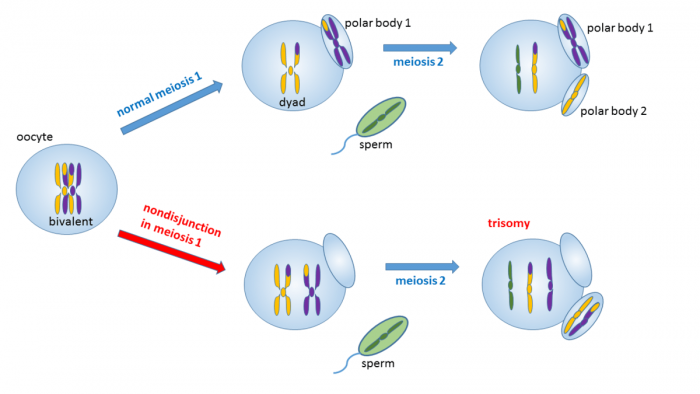
Biology Diagrams Nondisjunction occurs when chromosomes do not separate properly during cell division. This produces cells with imbalanced chromosome numbers. Chromosomal Abnormalities If a zygote is formed from a gamete that has experienced a non-disjunction event, the resulting offspring will have extra or missing chromosomes in every cell of their body Conditions that arise from non-disjunction events include: Patau's Syndrome (trisomy 13) Edwards Syndrome (trisomy 18) Down Syndrome (trisomy 21) Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY) Turner's Syndrome
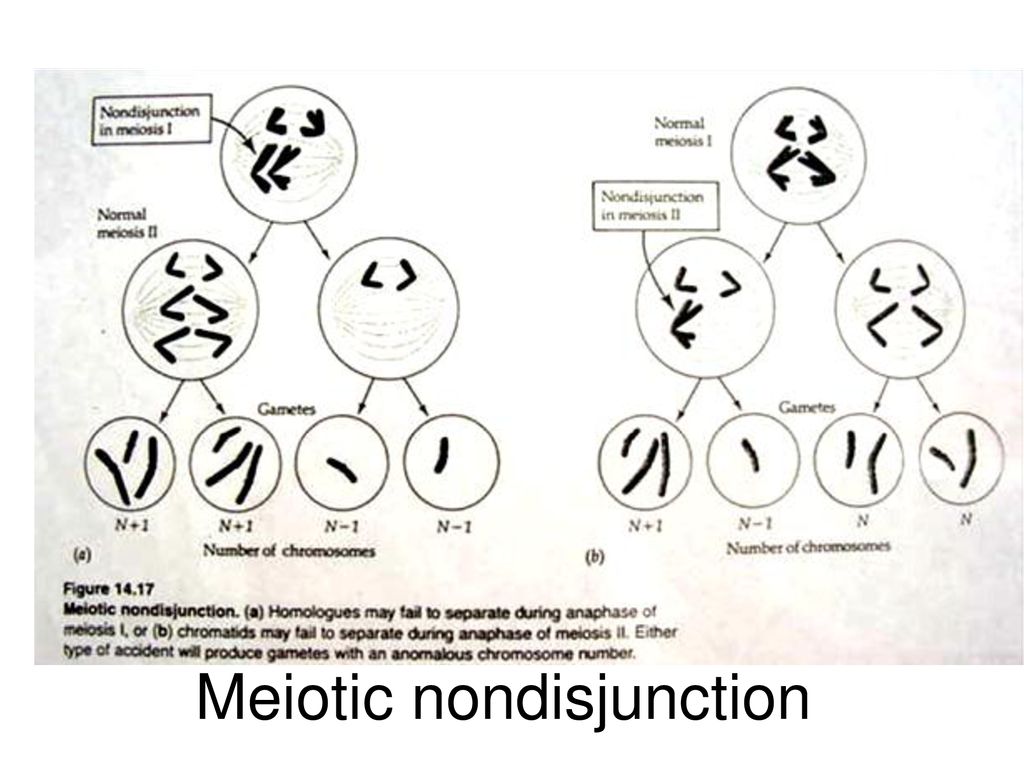
Meiotic nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes to segregate properly to opposite poles during meiosis resulting in the production of gametes that have an improper chromosome complement. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following accurately describes a possible meiotic nondisjunction event?, All of the following events occur during normal meiosis except _______., T/F In order to create the possibility of generating a trisomy, nondisjunction must occur during meiosis II. and more. Publisher Summary This chapter discusses the mechanisms of nondisjunction, with regard to the origin of aneuploidy, in mammalian germ cells at the molecular, cellular, and tissue levels. Developing germ cells appear to be especially sensitive to any environmental insult or to a chromosomal constitution that induces perturbations in the highly ordered timing of events in meiotic progression
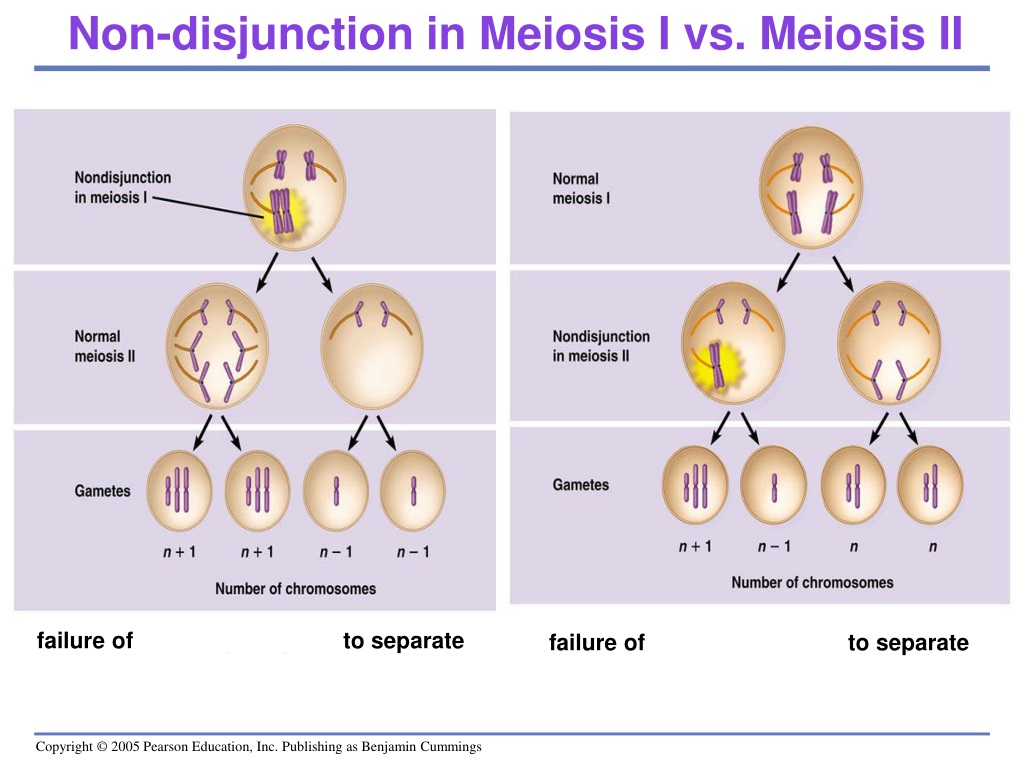
Genetics, Nondisjunction Biology Diagrams
Mitotic nondisjunction can cause somatic mosaicism, with the chromosome imbalance only reflected in the direct offspring of the original cell where the nondisjunction occurred. This can cause some forms of cancer, including retinoblastoma. Meiotic nondisjunction is of greater clinical significance since most aneuploidies are incompatible with life. In contrast, euploidy is when a cell contains the normal chromosome complement. Nondisjunction may occur any time a cell divides, so it can happen during mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II. Conditions associated with nondisjunction include mosaicism, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. Nondisjunction: Let's explore the science behind how an offspring acquires the wrong number of chromosomes through a deleterious phenomenon during meiosis.