brainstem I Diagram Biology Diagrams
brainstem I Diagram Biology Diagrams Get a diagram of human brain anatomy and key facts about this important organ. Home . Science Notes Posts; cerebellum, and brainstem, but these portions contain many key sections. and interactions with the world around us. Here is a look at the intricate anatomy of the brain, its functions, and the consequences of damage to different areas.

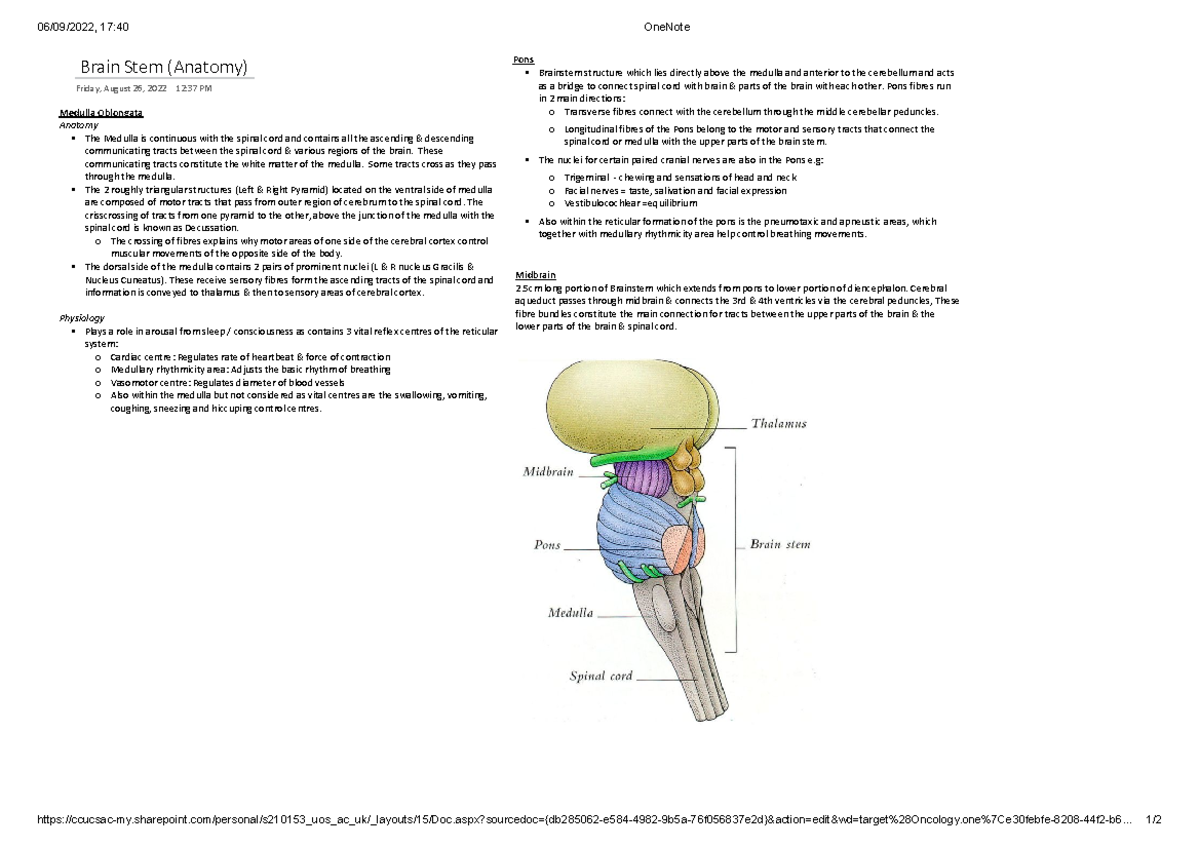
Brainstem Anatomy: Structures of the brainstem are depicted on these diagrams, including the midbrain, pons, medulla, basilar artery, and vertebral arteries. The medulla oblongata (myelencephalon) is the lower half of the brainstem continuous with the spinal cord. The brainstem is a vital structure that connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls many essential life-sustaining functions. It consists of three main parts: the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The brainstem acts as a conduit for motor and sensory pathways between the brain and body and contains nuclei that control basic autonomic processes such as heart rate, breathing, and

Brainstem: What It Is, Function, Anatomy & Location Biology Diagrams
The brainstem (brain stem) is the distal part of the brain that is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.Each of the three components has its own unique structure and function. Together, they help to regulate breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and several other important functions.All of these brainstem functions are enabled because of its unique anatomy; since the brainstem
• Recognize the major internal and external landmarks on the dorsal and ventral surface of the brain stem, so that you can determine if a gross or stained cross section is medulla, pons or midbrain. • Identify on a typical cross section all the brain stem nuclei containing motor neurons that end on striated muscle.

Boundless Anatomy and Physiology Biology Diagrams
Anatomy. The brain stem is a tube-shaped mass of nervous tissue a little over 3 inches (8 cm) long. It is located at the base of the brain, superior to the spinal cord and inferior to the cerebrum. As the brain stem ascends from the spinal cord, it widens and becomes more complex in its structures, both internally and externally.
