Derived Factors That Promote Pericyte Biology Diagrams
Derived Factors That Promote Pericyte Biology Diagrams The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.[1]Endothelium is of mesodermal origin. Both blood and lymphatic capillaries are composed of a single layer of endothelial cells called a monolayer. In straight sections of a blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells typically align and elongate in the direction of fluid flow.

1. Vascular Endothelial Cells. Vascular endothelial cells (VECs) are a type of endothelial cells that cover the inside walls of blood vessels, such as capillaries, veins, and arteries, and act as a protective barrier between the circulating blood and the surrounding tissues. Less is known about the induction of capillary fates; however, emerging evidence indicates that capillary endothelial cells are less of an established cell state than artery and vein endothelial cells, and might instead exist along a continuum, known as zonation 29,45,65-69. This zonation has been observed in capillaries in the brain and Endothelial Cells Line All Blood Vessels. The largest blood vessels are arteries and veins, which have a thick, tough wall of connective tissue and and many layers of smooth muscle cells (Figure 22-22).The wall is lined by an exceedingly thin single sheet of endothelial cells, the endothelium, separated from the surrounding outer layers by a basal lamina.

Capillaries: Continuous, fenestrated and sinusoidal Biology Diagrams
Capillary angiosarcoma. Rare cancer of the endothelial cells that can affect the capillaries. Capillary leak syndrome. A condition that causes a sudden drop in blood pressure. It sometimes requires emergency treatment. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. An inherited blood vessel disorder that causes abnormal growths (telangiectases) that The endothelium, a monolayer of endothelial cells, constitutes the inner cellular lining of the blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) and the lymphatic system, and therefore is in direct contact with the blood/lymph and the circulating cells. The term "endothelium" was first coined in 1865 by the Swiss anatomist, Wilhelm His [20,537]. Then, and thereafter up to the early 1970s
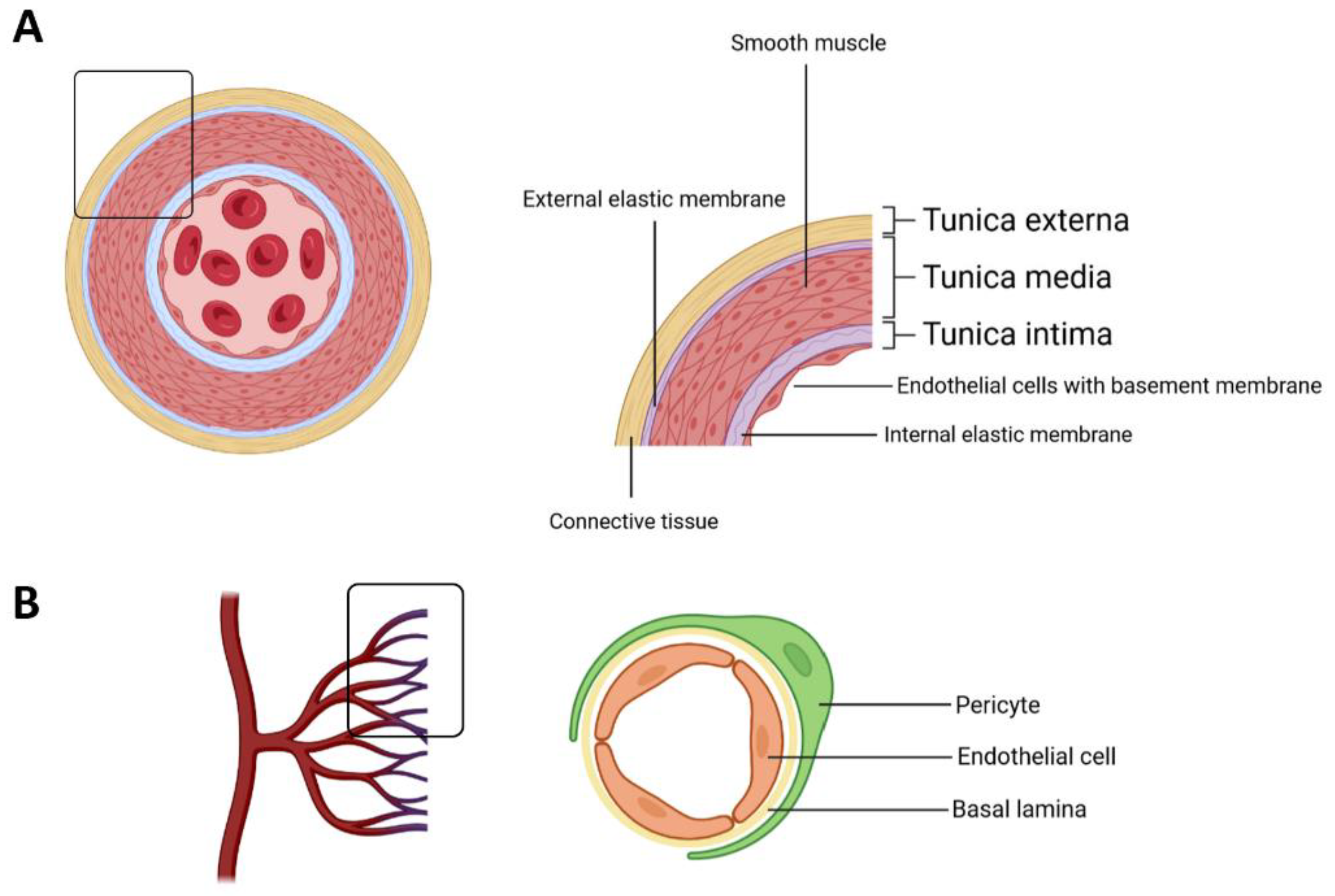
The vascular endothelium is the inner-most structure that coats the interior walls of arteries, capillaries and veins. Endothelial cells (EC) were described to anchor to an 80-nm-thick basal lamina (BL). Both EC and BL constitute the vascular intima, establishing a hemocompatible surface,

Endothelial Cells: Definition, Types, Structure, Functions Biology Diagrams
Continuous capillaries are generally found in the nervous system, as well as in fat and muscle tissue. Within nervous tissue, the continuous endothelial cells form a blood brain barrier, limiting the movement of cells and large molecules between the blood and the interstitial fluid surrounding the brain. Fenestrated
